Abbe Museum to Host First-Ever Kid’s Summer Camp
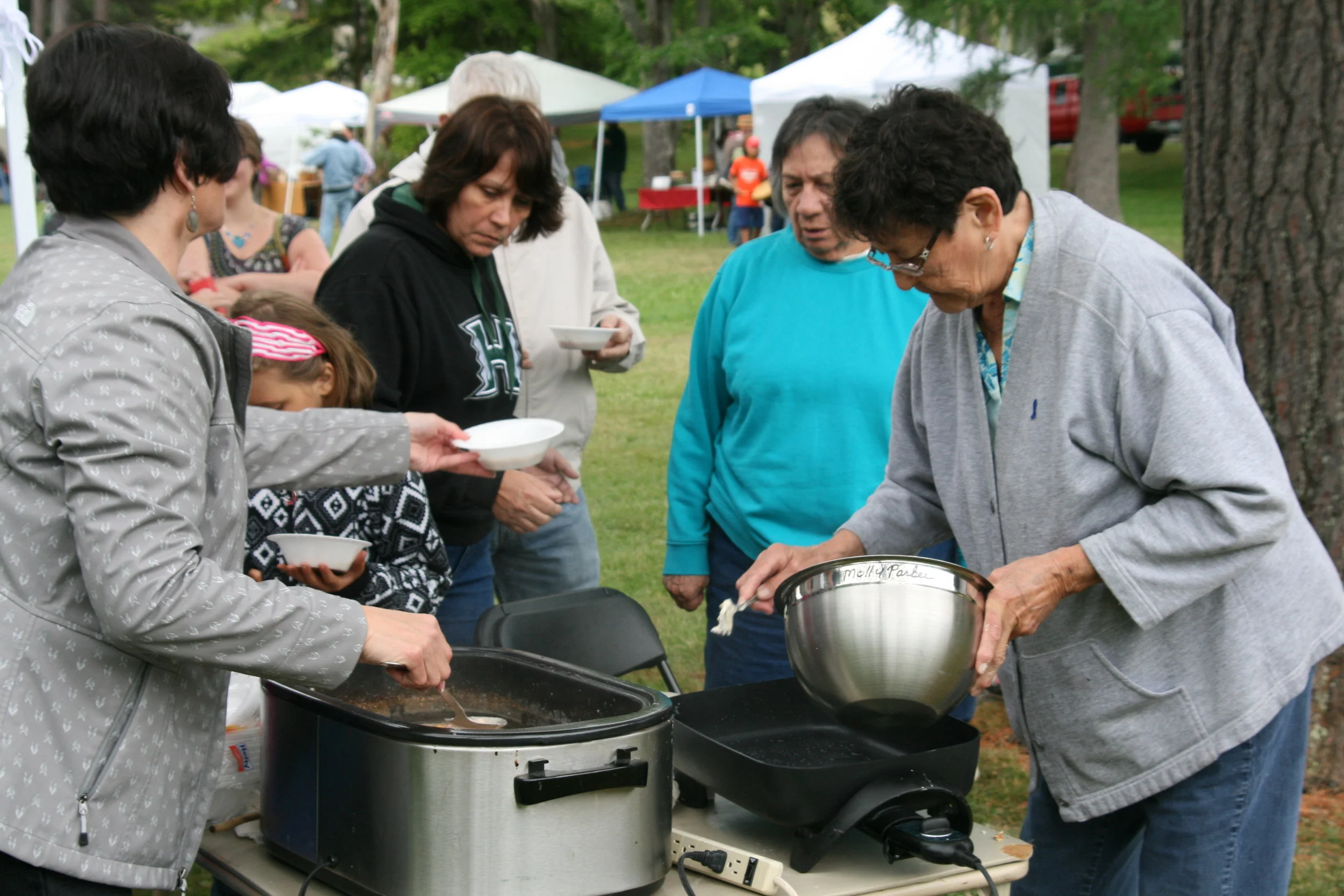
/The Abbe Museum is excited to announce the Abbe Museum Summer Camp, a children's day camp where highly-experienced museum staff and Wabanaki educators will oversee outdoor activities and educational opportunities for children ages 7-12. Scheduled for August 20-24, 2018, from 8 am – 3 pm, each day will be thematic with other camp activities mixed in to keep children active and engaged.
“We’re excited to offer this one-of-a-kind learning experience that sparks the imagination while offering plenty of fun,” said the Abbe’s Curator of Education, Starr Kelly. “The Abbe is dedicated to an inclusive and active education in order to foster a lifelong passion for learning. Campers will get to be chefs, scientists, artists, botanists, storytellers, and explore the rich and exciting world of the Abbe Museum’s two locations.”
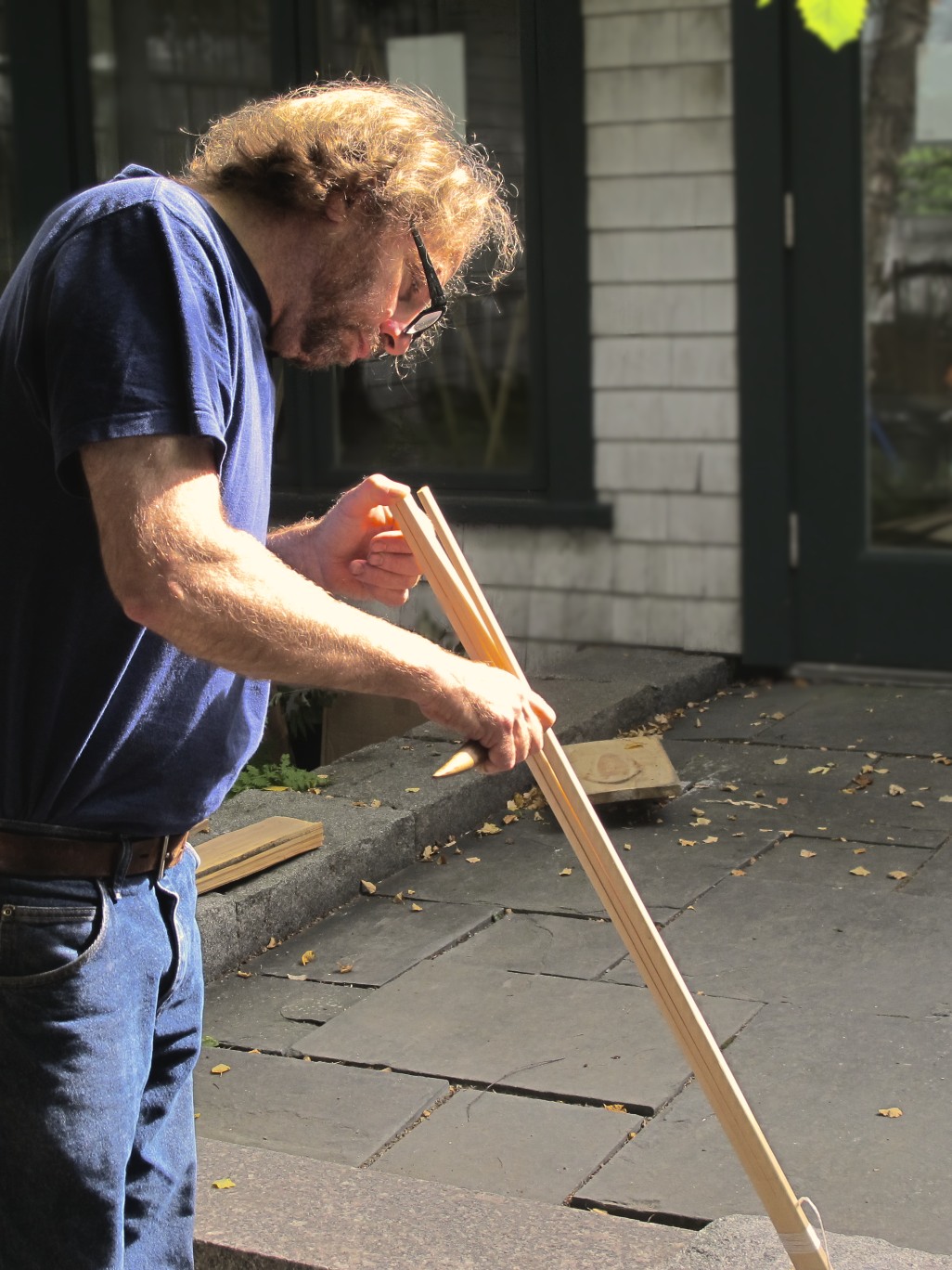
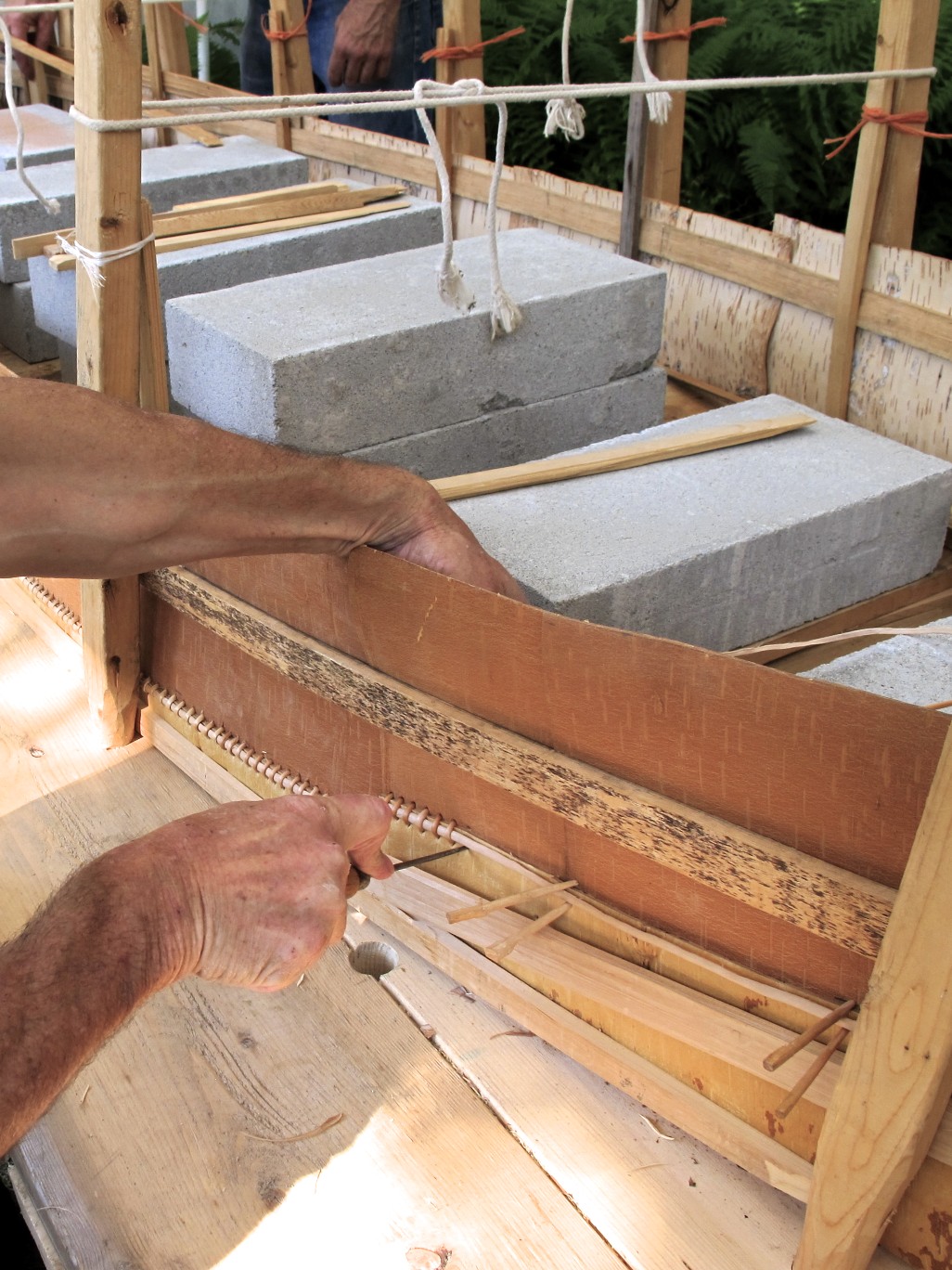
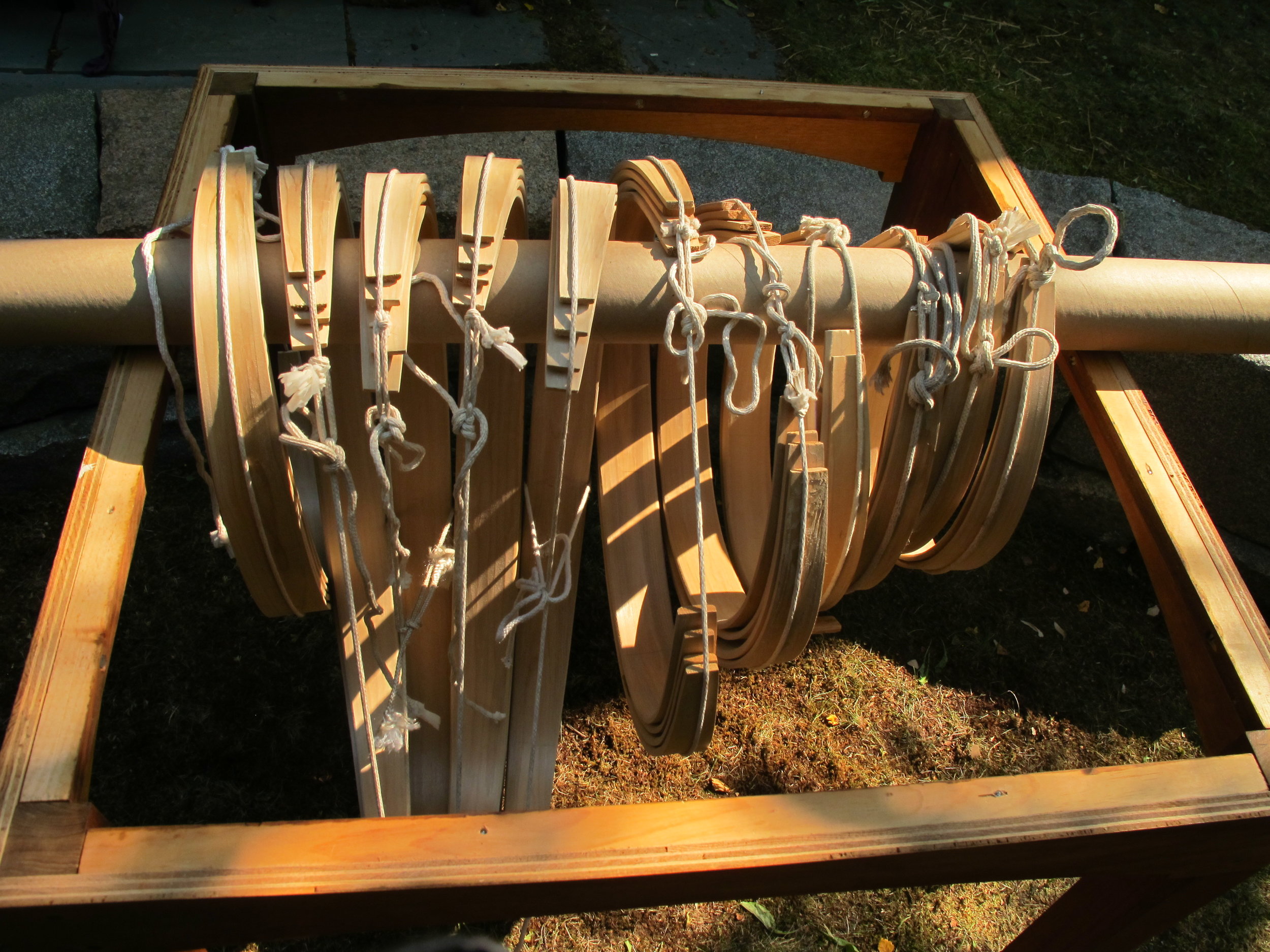
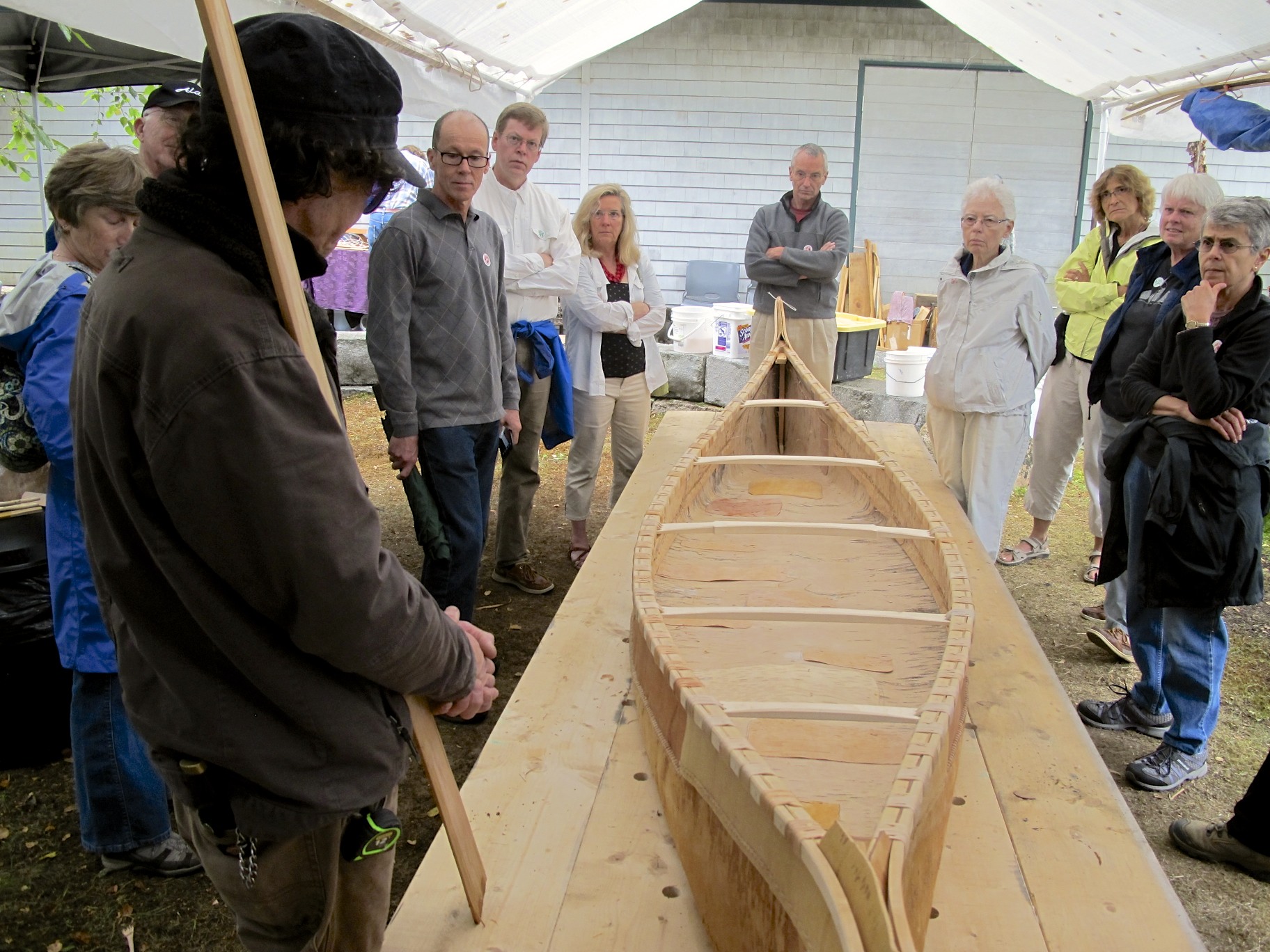
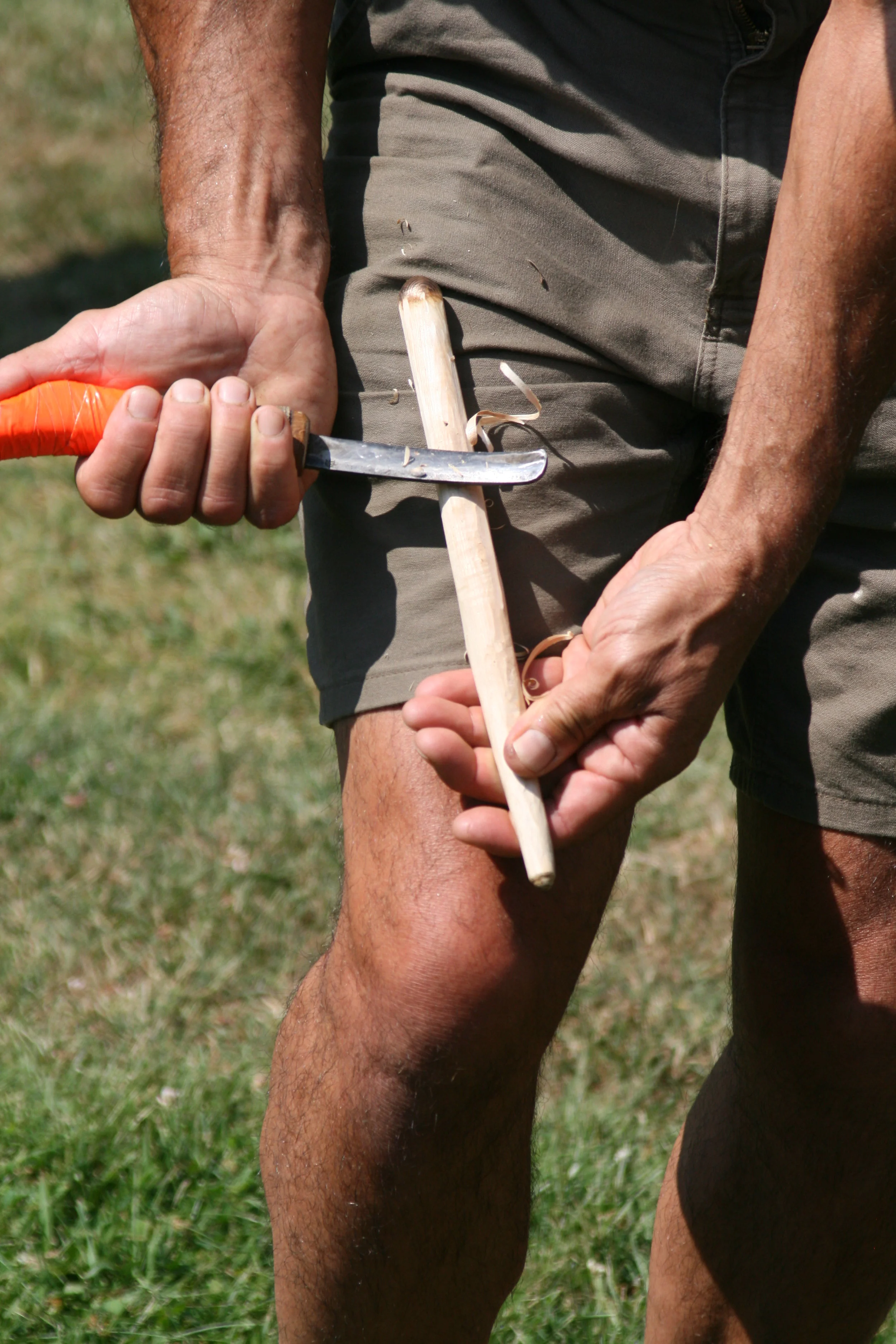
Throughout the week, segments will be dedicated to the pursuit of 12,000 years of history and culture in the Wabanaki homeland, allowing campers to work with the Museum’s educational collection as well as go on scavenger hunts and respond to art made by Wabanaki students.
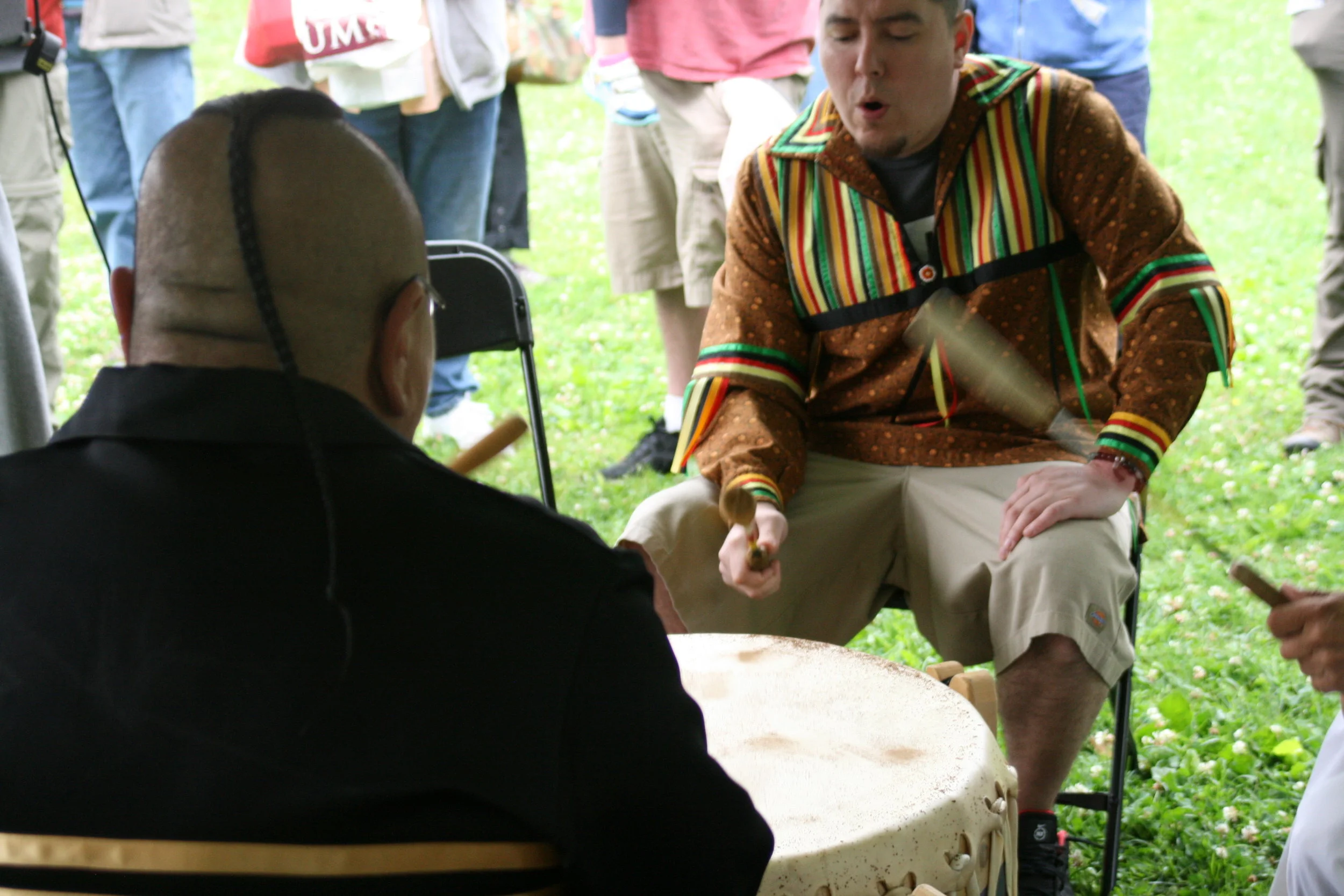
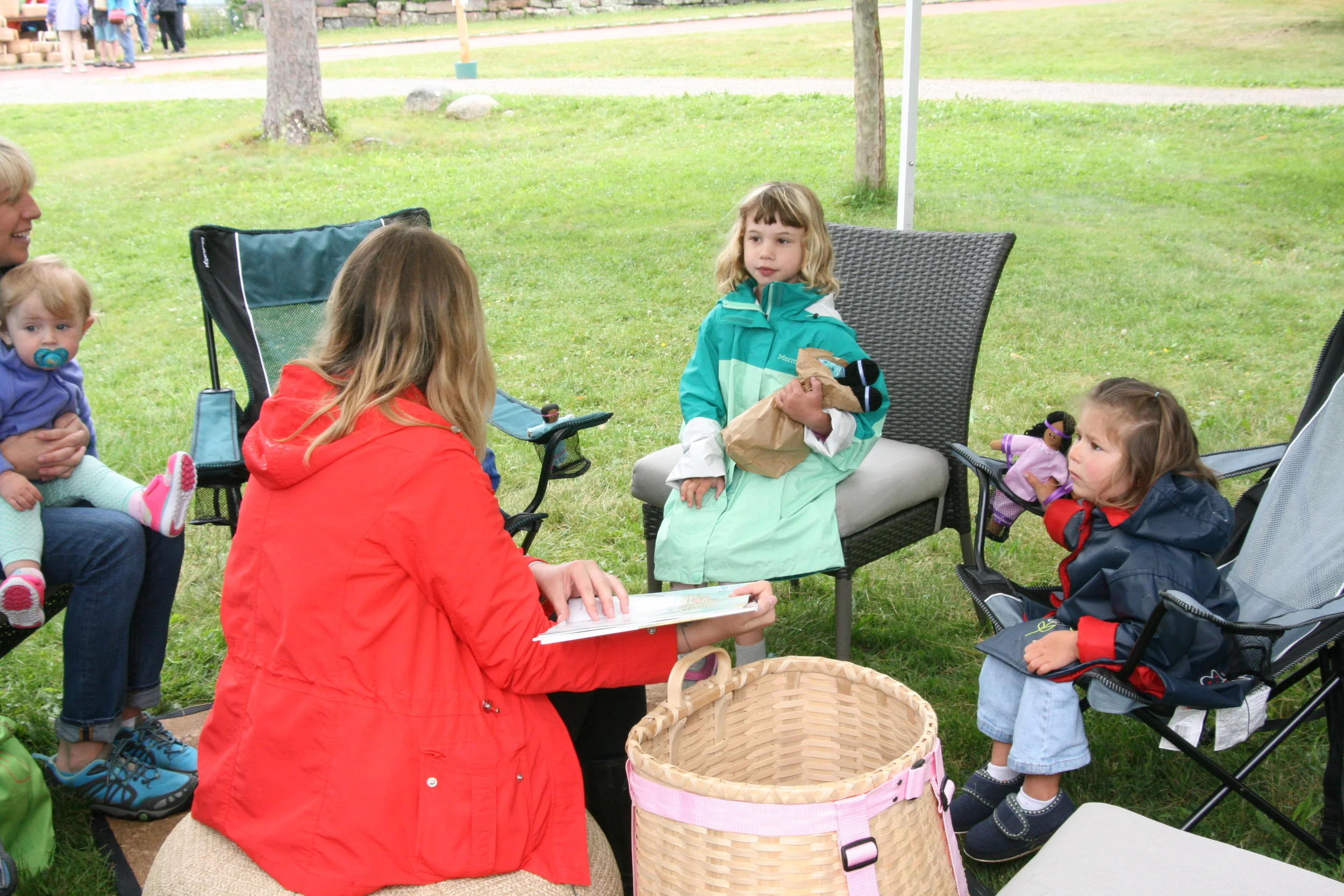
One day will celebrate Wabanaki storytelling traditions with a storyteller who will share stories the way they were meant to be shared: orally and within a community of people. Each camper will have the opportunity to create their own story and represent it visually, and all of the stories will be shared on the Abbe’s social media platforms.
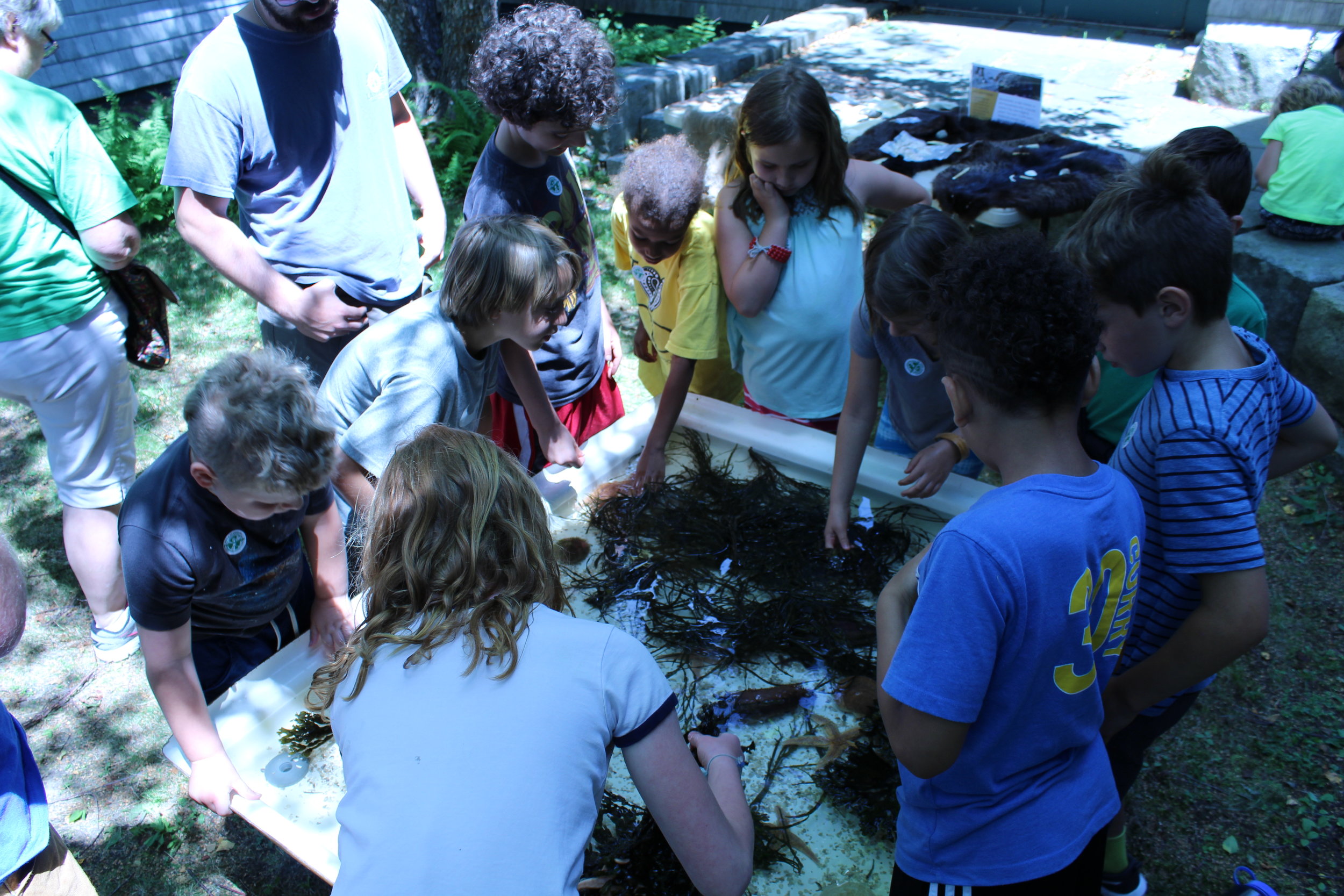
The Museum will delve into Wabanaki perspectives of science and environment by going on a hike inside Acadia National Park. Campers will learn to identify important plants that Wabanaki people harvest and use and will also learn about Indigenous foods of the Americas, participating in hands-on cooking experiences where they will even get to try some Native-inspired recipes. Campers will even get to produce and script their very own cooking segment.
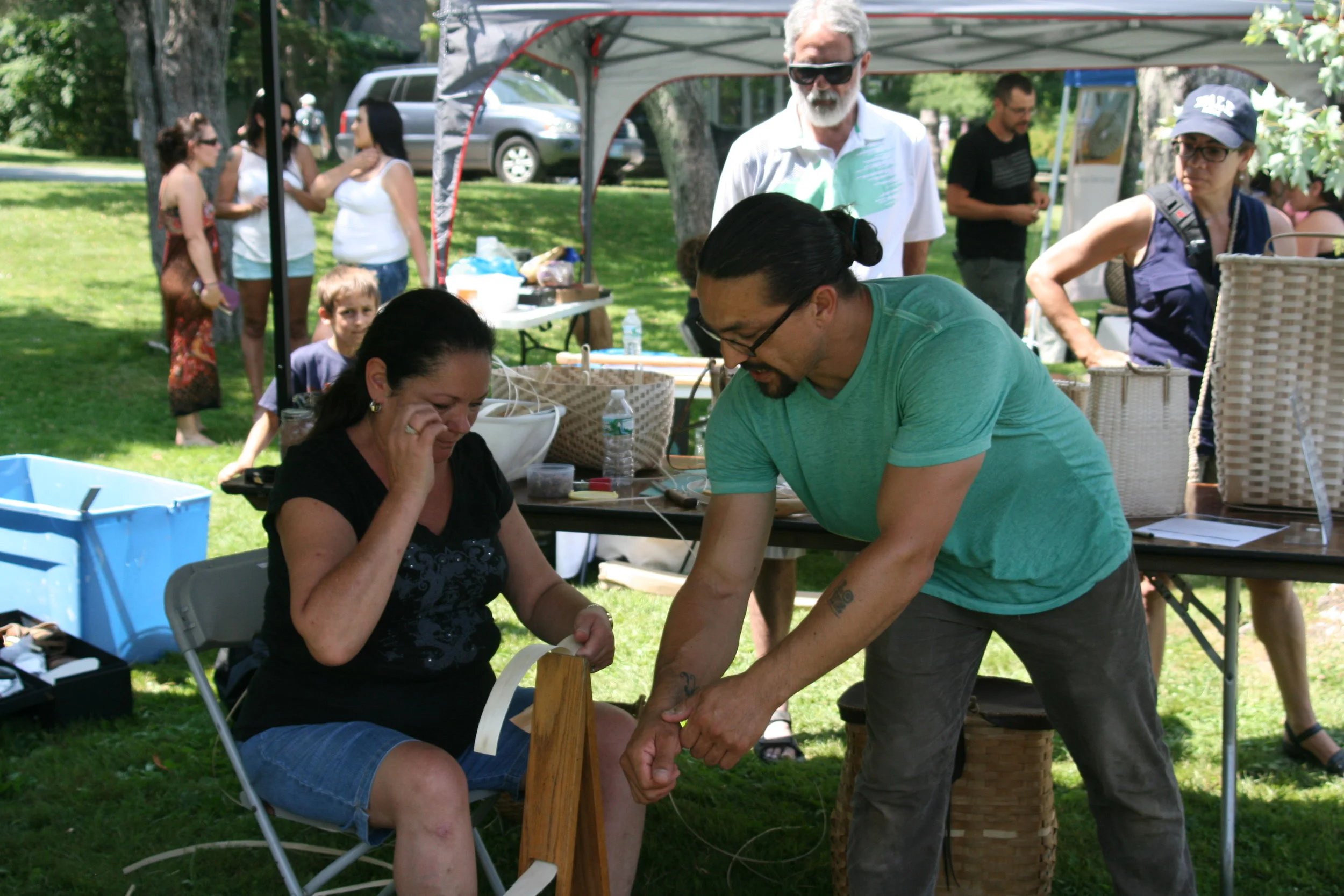
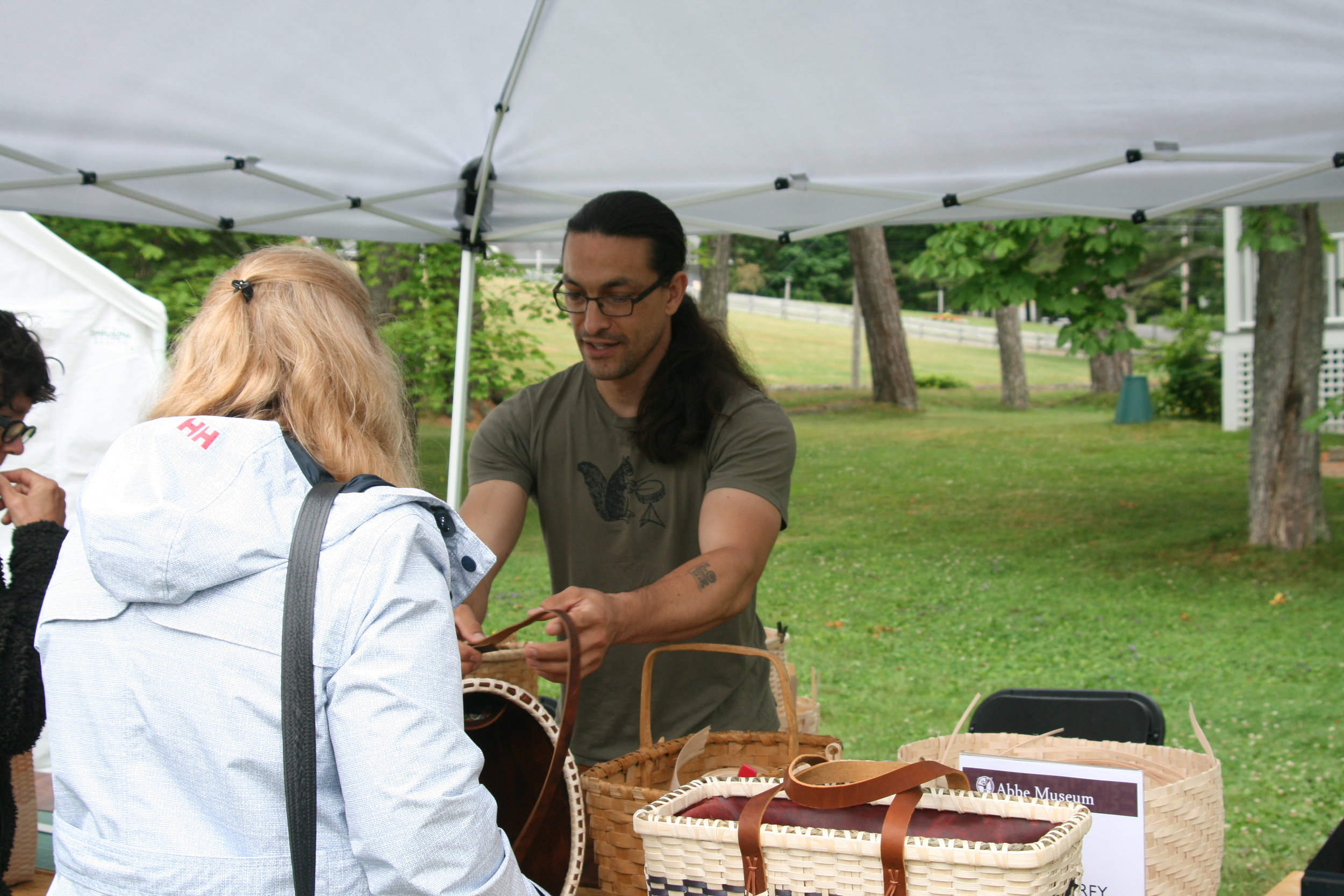
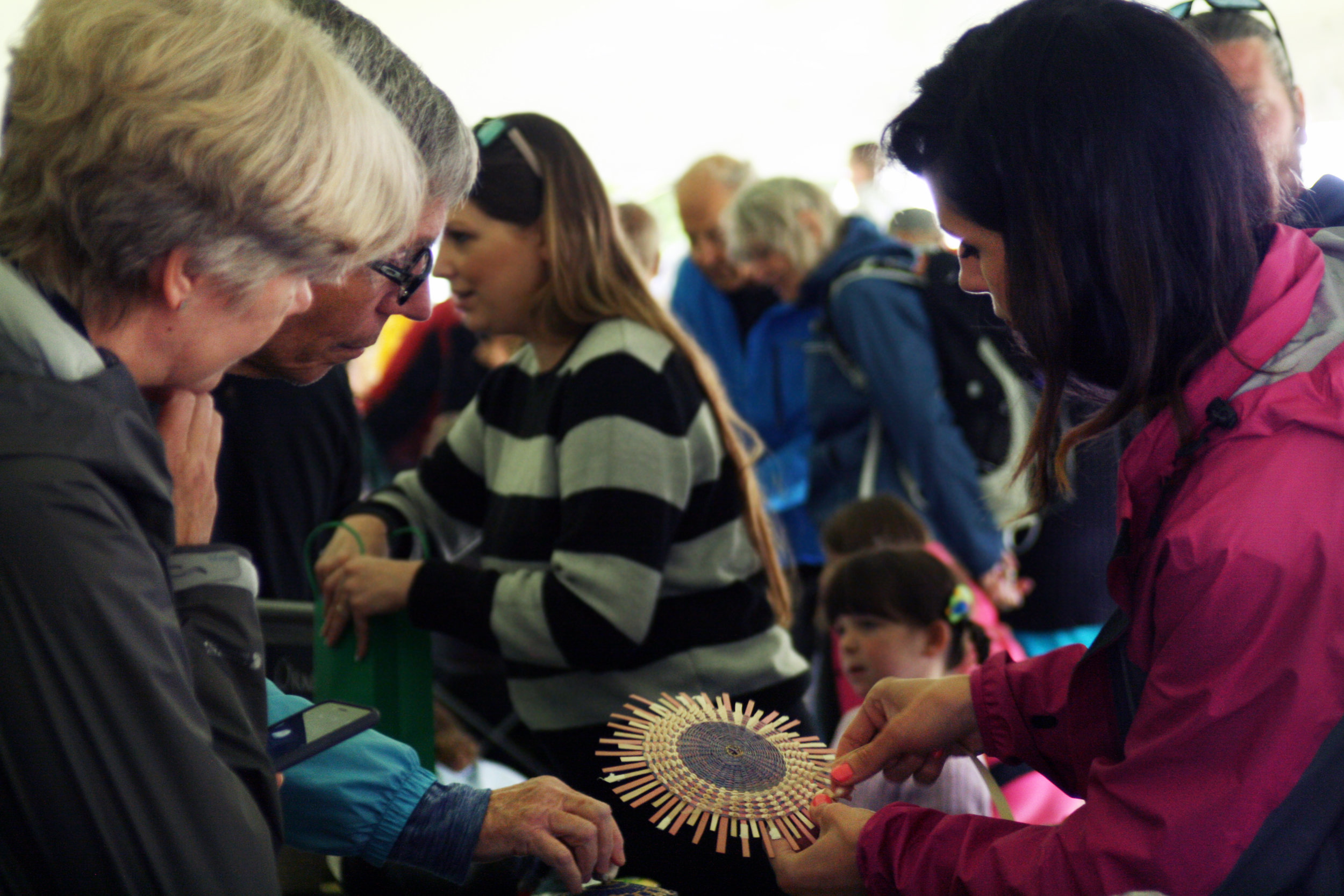
A day centered on the arts and the importance of traditions and expression will teach campers about traditional Wabanaki art forms, giving them the opportunity to make their very own masterpiece. They will get to handle items from the Museum’s collections as they learn more about the artists who made them.
Camp runs from August 20- 24 from 8 am- 3 pm, mostly at the Museum’s downtown Bar Harbor location at 26 Mount Desert St. The cost to attend is $200 for the week and the extended day program until 5 pm is $88 for the full week or $22 per day. To apply, please visit www.abbemuseum.org/programs and fill out a registration form and return it by May 15, 2018. Space is limited.